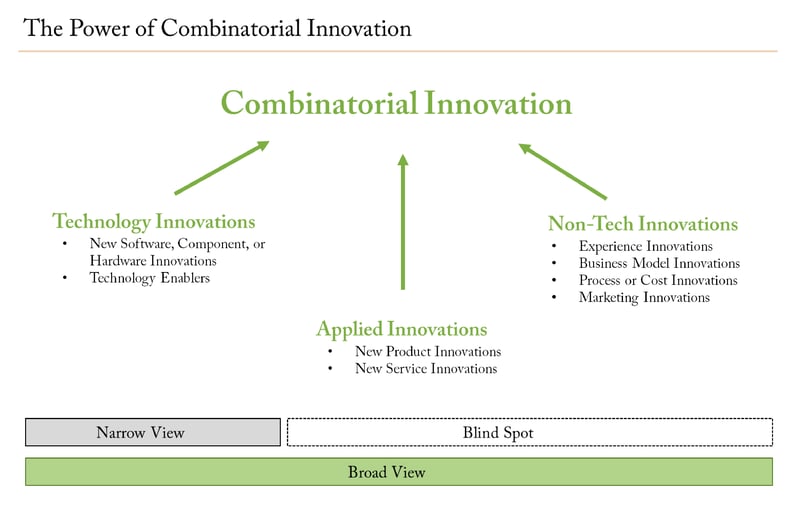
While technology can accelerate innovation, technology and innovation are not synonymous. Technology, such as new software, component, or hardware offerings (what some call “tech enablers”) is just one type of innovation employed by leading innovators to sustain growth.
As innovation investors, we cast a wider net in our search for leading innovators. We look both within and beyond the technology sector for innovations in products, services, distribution, business models, and other facets of a business that we think will make a profound impact on users, the company, and the industry.
Casting a Broader Net and Avoiding the Blind Spot
We believe in taking a broad view of innovation to avoid the “blind spot” that often results from a narrow, technology-only focus. This more encompassing perspective includes three categories of innovation: 1) Technology-based Innovations, 2) Applied Technology Innovations, and 3) Non-Technology Innovations (see chart below).
In industry after industry, we are seeing new tech-enabled business models that apply technology innovations to take market share and sustain leadership and growth. Notably, the most innovative companies combine technology innovations with non-technology innovations, such as brand/marketing innovations or business model innovation. Academics call this “combinatorial innovation,” and it is a key weapon leading innovators use to develop differentiated offerings that can take market share over time.
Thus, investment approaches that only—or primarily—focus on technology-based innovations may be missing out on important innovations arising in the applied technology and non-technology innovation areas. A limited focus could also lead to over-exposure to a narrow part of the economy or markets. At Evolutionary Tree, we build innovation-focused strategies that provide broader access to all three categories of innovation.
Assessing Innovation Impact
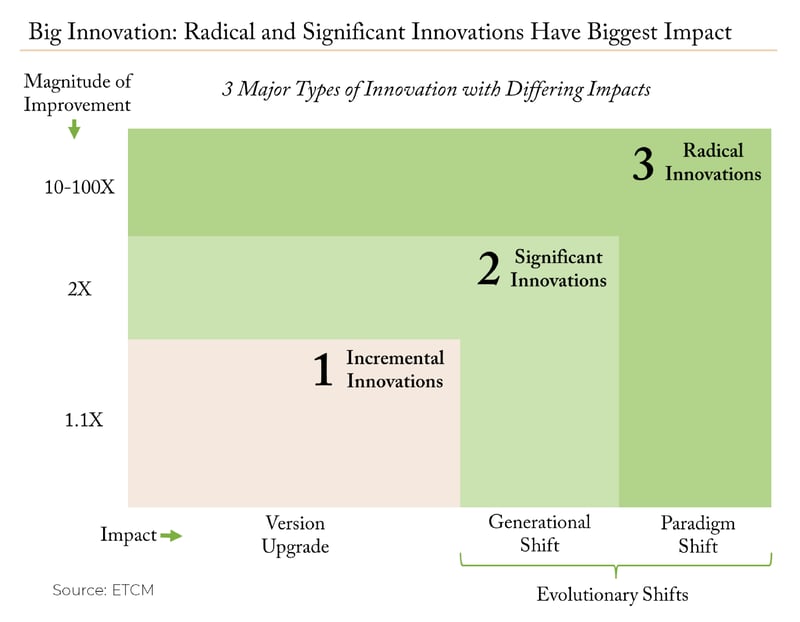
Determining the potential impact of innovations is another important part of our process. We categorize innovations as either incremental, significant, or radical.
Incremental innovations are the most common and have the smallest impact. They drive an upgrade from one version to another and often are replicated by competitors, conferring little in the way of competitive advantage. Significant and radical innovations drive large magnitudes of improvement for users and tend to create multi-year secular trends or evolutionary shifts. While significant innovations drive a generational shift, radical innovations are more disruptive and drive paradigm shifts. When selecting investments for our innovation-focused portfolios, we focus on significant or radical innovations that we believe have the potential for big and long-term impact.
Combine Innovations to Generate Combinatorial Innovation
The great innovators of our time combine multiple types of innovation to create highly differentiated offerings that enable them to take market share, have pricing power, and create growth drivers to fuel growth over a multi-year period. For example, while we don’t currently own Apple in our portfolios, it is an example of a company that combines amazing software and hardware (Technology Innovation) with well-designed products (Product Innovation) wrapped in unique packaging and branding (Brand/Marketing innovation) delivered in stores that offer great experiences such as the Genius Bar (Experience Innovation).
We actively seek out leading and emerging innovators that create these types of great innovation combinations, as we believe this is the best approach to add value for client portfolios over the long term. To fully appreciate these combinations, investors must expand beyond technology and look to multiple types of innovation that create that “magic” that delights consumers.
Examples of portfolio holdings and the different types of innovation they demonstrate:
Technological Innovation: HubSpot
HubSpot built the leading marketing automation software-as-a-service platform for small and mid-sized businesses. It combines this Technological Innovation with Experience Innovation in that it focuses on a great user interface (UI) that offers amazing ease of use; it also combines this with Business Model Innovation with its subscription-based model and its freemium model, a business model that offers basic features at no cost and charges a premium for supplemental or advanced features. HubSpot is enabling small businesses to create and deploy sophisticated digital marketing campaigns that allow them to compete with larger companies.
Product Innovation: Axon
Axon has generated a series of Product Innovations to bring technology to the field of law enforcement. The goal is to help modernize police departments and shift to less or non-lethal weapons, supported by software-based solutions to improve officer productivity and accountability. Best known as the company that innovated the Taser, Axon has developed a number of additional product innovations, including Axon body and in-car cameras and cloud-based evidence and records management systems. Axon is a great example of a company combining hardware, software, and cloud-based innovations to improve law enforcement efficiencies, accountability, and outcomes.
Service or Experience Innovation: Bumble
Bumble created an online dating app that provides women with a more empowering, better dating experience relative to other dating apps by allowing them to be the first to initiate messages with matches. This functionality is an important feature of the app, which also enables additional safety features that enforce accountability, reducing the Wild West element seen in other apps. Bumble combines this Experience Innovation with Technology Innovation in that its apps enable video chat. Bumble is seeing success with these innovations as it expands to more and more countries around the world.
Process or Cost Innovation: Amazon
Amazon Web Services (AWS) invented the concept of Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), which offers significant cost benefits to customers. Given its scale, Amazon can offer lower computing/storage costs, resulting in Cost Innovation. The company combines many types of innovation on both AWS and its e-commerce site, such as database-as-a-service or analytics on AWS or next-day delivery or Prime Video on the e-commerce side. Like Apple, Amazon is a quintessential example of the combination of many different types of innovation, which, in turn, create entire ecosystems of products and services.
Marketing or Brand Innovation: Farfetch
Farfetch is the leading global e-marketplace for luxury products, offering 28 of the top 30 luxury brands on its multi-brand e-commerce site. The company partners with a number of luxury brands using its e-concession model that allows the brands to control pricing and product marketing on its site (Brand Innovation), taking a 30% commission on products sold on its e-marketplace without carrying the inventory. Farfetch powers many of the luxury brands online by assisting with website development, logistics, and customer service (Business Model Innovation and Technology Innovation).
Business Model Innovation: Twilio
Twilio is the leading Communication Platform-as-a-Service (CPaaS) that allows companies to add various communication functionality to applications, such as messaging, email, video, or voice. Underlying its platform is an application programming interface-based (API) platform that allows developers to add discrete communication features to their custom-built applications, an important Business Model Innovation. APIs are the new building blocks of software applications. Instead of having to build applications from scratch, developers can stitch together APIs to build applications much more quickly and easily, all while improving security.
Organization Innovation: Sarepta
Sarepta is a leading biotech firm for neuromuscular disease. It uses an “open innovation” organization mode of innovation development by establishing a large number of partnerships with leading medical hospitals (such as National Children’s Hospital) or smaller biotechs to access innovations and insights into multiple neuromuscular diseases, such as Duchenne’s Muscular Dystrophy (Organization innovation). Sarepta has developed two biotechnology platforms that support a broad and growing drug pipeline, with its exon-skipping and gene therapy tech platforms (Technology Innovation).
Innovation Diversity is What Differentiates Us
These examples are evidence that, although technology is a key component used to create new innovations, innovation is not exclusive to just technology. At Evolutionary Tree, our portfolios are a mix of innovative businesses across the economy. This diversity across innovation categories and types is a key element of what differentiates us from other innovation strategy offerings or traditional tech funds, which, because they are often narrowly focused on technology innovation, may be overlooking other types of innovation.
We invite you to learn more about our unique approach to investing in innovation by reading the collection of white papers and thought pieces we’ve written and published on our website.